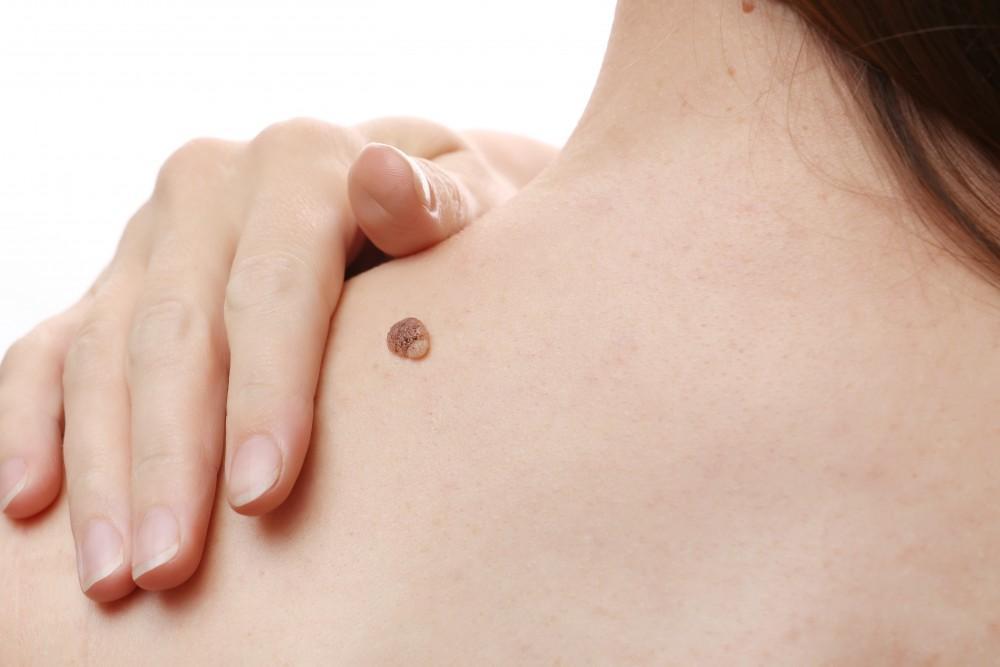
Understanding Skin Cancer
Skin cancer develops when skin cells begin to grow uncontrollably due to DNA damage, often caused by exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation. There are several types of skin cancer, including:
- Basal Cell Carcinoma (BCC)
- Squamous Cell Carcinoma (SCC)
- Melanoma
Among these, basal cell carcinoma is the most common and is generally slow-growing. Detecting basal skin cancer early stages can greatly reduce the need for invasive treatments.
Skin Cancer Pictures Early Stages
Knowing what to look for can make a major difference. Early stage skin cancer may appear as:
- Small, shiny or pearly bumps (especially for BCC)
- Flat, scaly, or crusty patches
- Dark brown or black lesions with irregular borders
- Red or pink growths with a raised edge
You can find reliable skin cancer pictures early stages from trusted dermatological sources, which can help you recognize potential problems and prompt early intervention.
Types of Skin Cancer
Here is a brief overview of the types of skin cancer you should know:
Basal Cell Carcinoma (BCC)
- Most common form of skin cancer
- Usually found on sun-exposed areas (face, neck)
- Appears as a translucent bump or patch
Squamous Cell Carcinoma (SCC)
- Second most common
- May look like a rough, scaly patch or open sore
- Typically found on face, ears, neck, and hands
Melanoma
- Less common, but most dangerous
- Can develop anywhere on the body
- Often appears as an asymmetrical mole with uneven coloring
Early Stage Skin Cancer Screening
Regular screening is crucial. Early stage skin cancer screening can include:
- Full-body visual exams by dermatologists
- Dermatoscopic imaging
- Biopsies of suspicious lesions
- AI-assisted digital mole tracking
If you’re at high risk (e.g., fair skin, history of sunburn, family history), annual screenings are highly recommended.
Risk Factors for Skin Cancer
Some people are more prone to developing early stage skin cancer. Common risk factors include:
- Frequent sun exposure or tanning bed use
- Light skin, freckles, or red hair
- A weakened immune system
- History of sunburns
- Age over 50
Knowing your risk can encourage proactive care and early detection.
Preventive Measures
Preventing skin cancer is possible with the right habits:
- Use broad-spectrum sunscreen SPF 30+ every day
- Wear protective clothing and hats
- Avoid peak sun hours (10 AM to 4 PM)
- Perform monthly skin self-exams
- Avoid indoor tanning
Treating Early Stage Skin Cancer
When caught early, treatment is often highly effective. Options for early stage skin cancer include:
- Cryotherapy: Freezing off abnormal cells
- Topical medications: Imiquimod or 5-fluorouracil for superficial cancers
- Excisional surgery: Cutting out the cancerous tissue
- Mohs surgery: A precise method for facial and high-risk areas
Each case requires a personalized approach. Dermatologists will determine the most effective course based on the type and location of the cancer.
Basal Skin Cancer Early Stages
Basal skin cancer early stages may not cause discomfort, making visual exams crucial. They may appear as:
- A persistent, non-healing sore
- A small bump that bleeds or crusts
- A scar-like area without injury
Early treatment of BCC can prevent larger lesions, deeper invasion, and disfigurement.
When to See a Dermatologist
You should seek professional care if you notice:
- A new mole or lesion that looks unusual
- A sore that doesn’t heal in 2–3 weeks
- Changes in size, shape, or color of a mole
- Any lesion that itches, bleeds, or becomes tender
Prompt attention ensures a higher success rate and fewer complications.
Living with Skin Cancer
After treatment for early stage skin cancer, many patients live long, healthy lives. Long-term steps include:
- Regular follow-up appointments
- Continued sun protection
- Monitoring for new growths
- Support groups or counseling if needed
Your skin health can be preserved with vigilance and early intervention.
Conclusion: Take Action Today
Early stage skin cancer is treatable, especially when detected early. With the right awareness and screening, you can significantly lower your risk of serious complications. If you’re concerned about changes in your skin or want to begin a screening routine, contact a board-certified dermatologist today.
Stay informed, stay protected, and prioritize your skin health.
